Train Station Design stands as a critical node in urban infrastructure, facilitating the seamless movement of the masses. Train station design is a highly technical discipline, embodying the convergence of civil engineering, urban planning, and operational efficiency. This technical guide navigates the intricacies of train station design, dissecting each step from blueprint to execution. This exploration not only delineates the execution process but also emphasises continuous improvement, ensuring that train station designs stand as paragons of technical excellence in urban infrastructure.

Here is a 12-step guide to how to design a train station:
Step 1: Define the Purpose and Scope
Before delving into the train station design process, it’s essential to define the purpose and scope of the train station. Consider factors such as expected footfall, types of trains, and the array of services the station will offer. This initial step sets the tone for the entire design process, ensuring that every element caters to the specific needs of passengers and operational requirements.
Step 2: Types of Train Station
Understanding the diverse types of railway stations is pivotal in tailoring design to specific needs. This classification considers factors such as territorial size, geographic location, functions, frequency of use, level of service, role in the urban transport network, and traffic range.
1. Territorial Size:
Railway stations can vary in territorial size, ranging from expansive hubs sprawling across extensive areas to more compact stations confined within limited space. The size of the territory significantly influences layout planning and design considerations.
2. Geographic Location:
Stations are often categorised based on their geographic location. Suburban stations serve the outskirts, city access stations connect urban peripheries, and city centre stations act as focal points within urban landscapes.
3. Functions:
Classifying stations by their functions helps in determining the specific services they offer. This includes categorising stations based on whether they primarily serve as terminals, junctions, or halts, influencing design elements such as platform allocation and passenger flow.
4. Frequency of Use:

Stations are categorised based on the volume of incoming passengers per day.
- Type 1 (very large) – over 50,000 passengers daily
- Type 2 (large) – 30,000 passengers
- Type 3 (medium) – 10,000 to 30,000
- Type 4 (small) – less than 10,000 passengers daily.
6. Role in Urban Transport Network:
Identifying whether a station is a central hub connecting various modes of transportation or serving as a terminal for specific routes, this classification guides the integration of the station into the city’s overall transit system.
7. Traffic Range:
Stations are also categorised based on the range and nature of traffic they handle. This includes differentiation between long-distance traffic, a combination of long-distance and regional traffic, high and medium regional traffic, and stations catering to low regional traffic. Each category influences design considerations related to platform capacity, waiting areas, and service offerings.
Incorporating these classifications early in train station design ensures a tailored and efficient approach, optimising functionality for each station type.
Step 3: Conduct Site Analysis
The second crucial step involves comprehensively analysing the chosen site. This encompasses an examination of the topography, accessibility, and surrounding infrastructure. Understanding the site’s context provides invaluable insights for efficient layout planning and influences decisions regarding entrances, exits, and connectivity with other modes of transportation.
Step 4: Design of Station Zones

Divide the station into zones based on functionality. Delineate areas for ticketing, waiting, boarding, and commercial spaces. Efficient zoning ensures a smooth flow of passengers and optimises the use of space. It also contributes to enhanced passenger experience and operational efficiency.
Step 5: Prepare Structural Plans
Collaborate with architects and engineers to develop detailed structural plans. Prioritise safety, durability, and compliance with building codes. These plans are the backbone of the entire project, ensuring the station’s longevity and resilience against environmental factors. A robust foundation guarantees the structural integrity of the station.
Step 6: Incorporate Accessibility Features
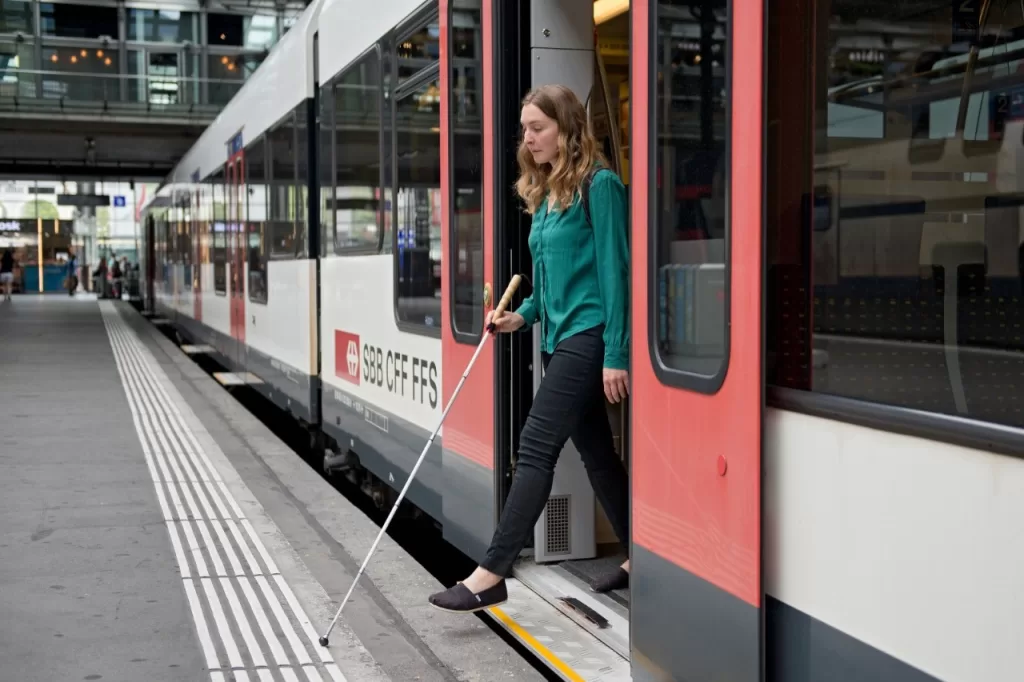

Designing with inclusivity in mind is not just a trend; it’s a necessity. Implement features such as ramps, elevators, and tactile paving to ensure accessibility for all passengers, including those with disabilities. Creating a station that is user-friendly for everyone contributes to a more inclusive and accommodating public space.
Step 7: Energy-Efficient Design
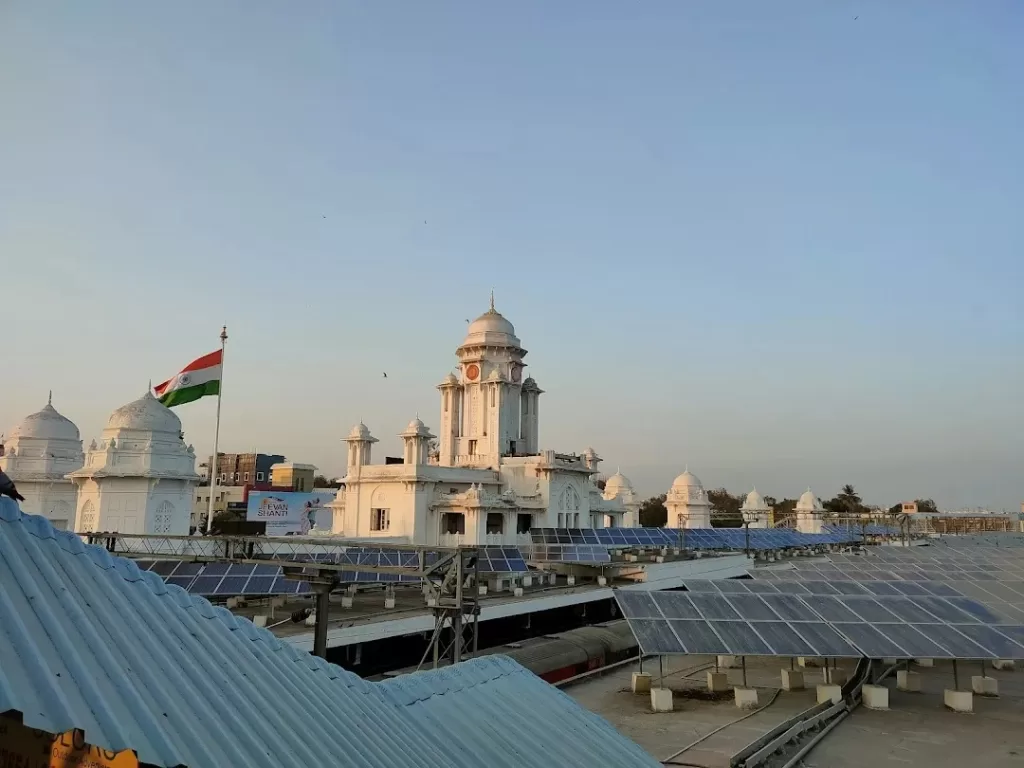

In an era where sustainability is a global priority, integrating energy-efficient design practices is paramount. Explore ways to harness natural light, incorporate energy-efficient systems, and consider renewable energy sources. Beyond reducing operational costs, a green design aligns with broader efforts towards a more sustainable future.
Step 8: Technology Integration
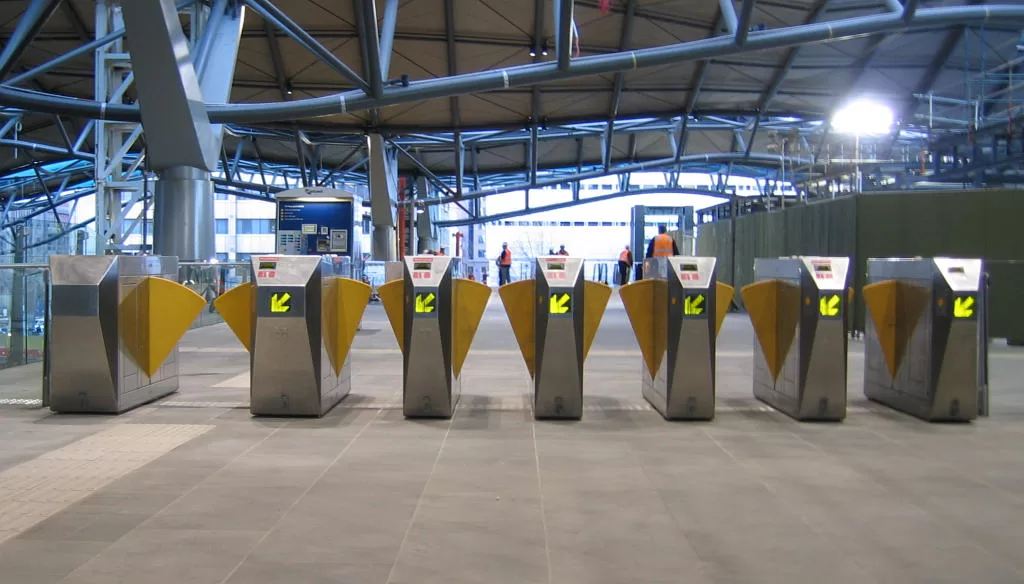

Embrace the power of technology to enhance both the passenger experience and operational efficiency. Implement smart ticketing systems, real-time information displays, and automated services. Technological advancements play a pivotal role in shaping modern, efficient train stations, providing passengers with a seamless and streamlined experience.
Step 9: Safety and Security Measures
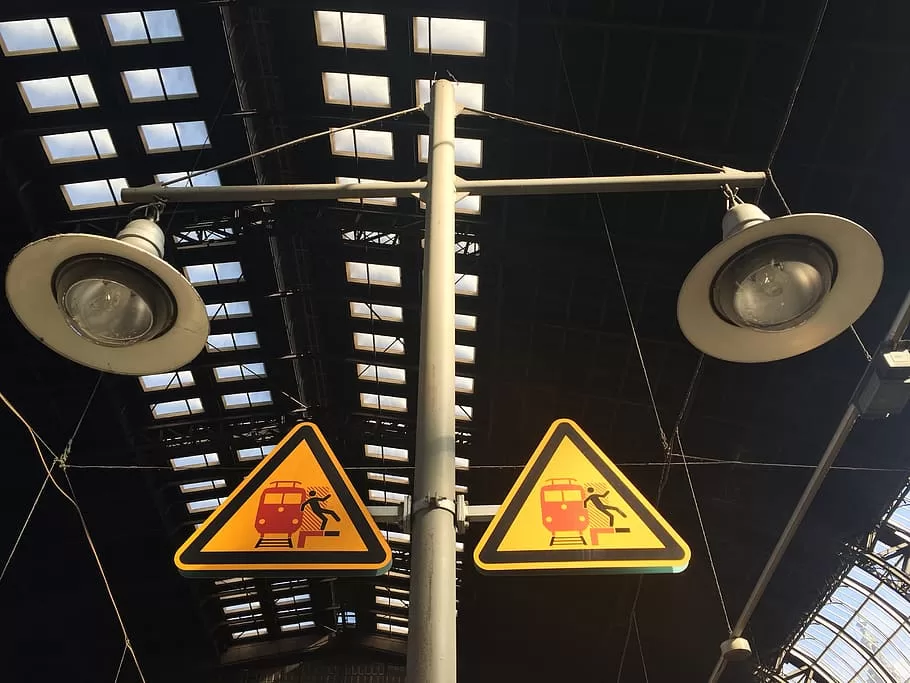

Passenger safety is non-negotiable. Well-designed emergency exits, visible signage, and efficient crowd management strategies are imperative. Collaborate with security experts to integrate state-of-the-art surveillance and emergency response systems. A secure environment is fundamental to instilling confidence in passengers and creating a safe travel experience.
Step 10: Aesthetic Appeal
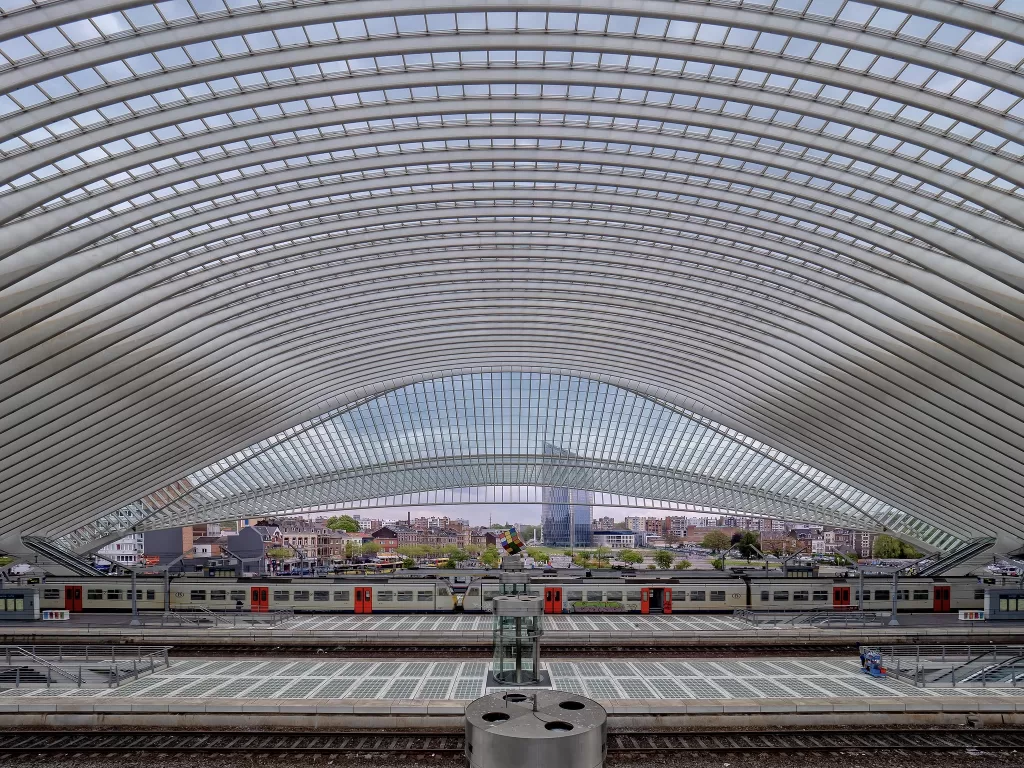

Balancing functionality with aesthetics is an art. Incorporate pleasing architectural elements, thoughtful landscaping, and even public art installations to create a welcoming atmosphere. A visually appealing station contributes to the overall positive experience for passengers, making the journey more enjoyable and memorable.
Step 11: Budgeting and Cost Management
A crucial aspect of any design project is realistic budgeting. Consider construction costs, materials, and labour in your financial plan. Implement effective cost management strategies to ensure the project stays within budget without compromising on quality or functionality. A well-managed budget is key to the success of the project.
Step 12: Execution and Continuous Improvement
The final step involves the meticulous execution of the design plan. Monitor progress, address challenges promptly, and ensure that the project stays on course. Post-construction, gather feedback from commuters and stakeholders, facilitating continuous improvement for future projects. Learning from each experience enhances the effectiveness of future train station designs.
Building Regulations in India: Brief Pointers
Amidst the creative and technical aspects of train station design, it’s crucial to navigate the landscape of building regulations in India. Adhering to the National Building Code (NBC), Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), and other relevant guidelines is non-negotiable. Collaboration with local authorities and regulatory bodies is essential for a seamless approval process, ensuring that the design aligns with the legal framework.
In conclusion, train station design is an amalgamation of operational efficiency and passenger-centric functionality. Each meticulously planned step, from defining purpose to integrating advanced technology, underscores the technical precision required in crafting modern transportation hubs. These train station designs stand as beacons of urban connectivity, where structural resilience, accessibility features, and energy-efficient systems converge seamlessly. The technical landscape of train station design, an ever-evolving frontier, emphasizes not just the completion of a project but a commitment to continuous improvement. As we navigate towards a future of interconnected cities, the legacy of technical excellence in train station design remains pivotal in shaping the urban experience.
Content Writing And Research By: Ar. Kiran Rathi
The post Train Station Design: An Easy And Comprehensive Guide appeared first on The Architects Diary.
Leave a Reply